Perugia smart city
the innovative digital transformation project of the Umbrian city
The city of Perugia, the capital and economic, social and cultural centre of the Region of Umbria, has a population of around 165,000 inhabitants, a vast territory that requires efficient and timely services and a continuous construction of communication channels between the public administration and citizens.

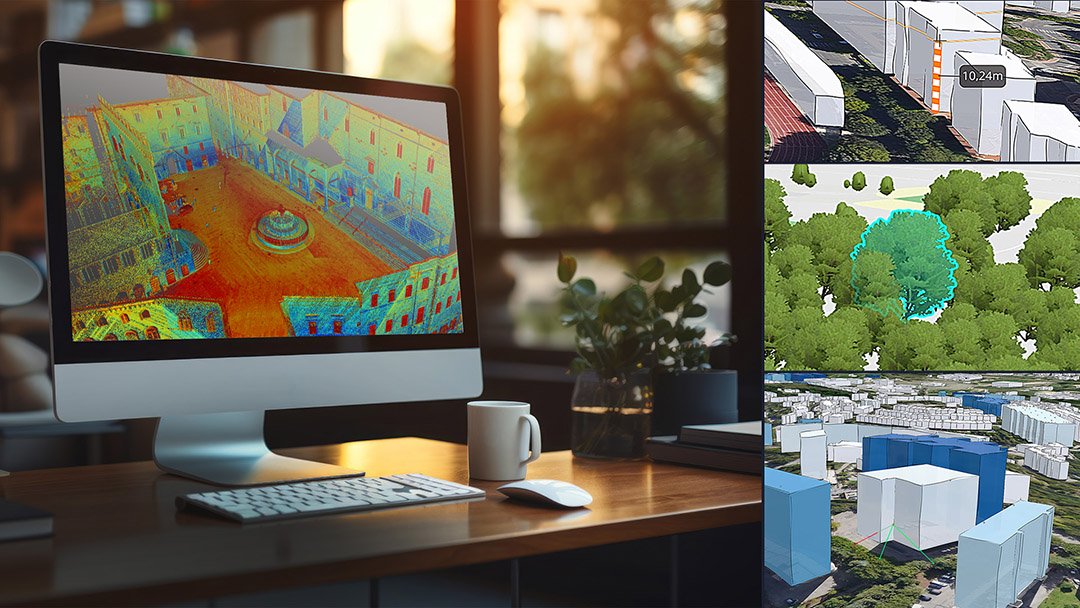
The municipality of Perugia needs, in the perspective of creating governance oriented to the needs of citizens and the efficiency of the PA, to find a technological system that guarantees an efficient collection and management of the city’s data with the integration of IoT services and technologies, a decision support system and tools to promote the active participation of citizens. It is a digital infrastructure capable of integrating the technologies already implemented in the municipality: the city is already equipped with a wide range of devices and sensors, but the benefits of all these technologies are so far marginal, as they produce a huge amount of unrelated data that is too complicated to process and results in a significant waste of time, money and resources.
At the end of the Urban Agenda project consultations, the choice of the city of Perugia fell on WiseTown and its smart city enabling infrastructure, based on FIWARE technology and capable of responding to new infrastructure needs.
technological innovation for the city
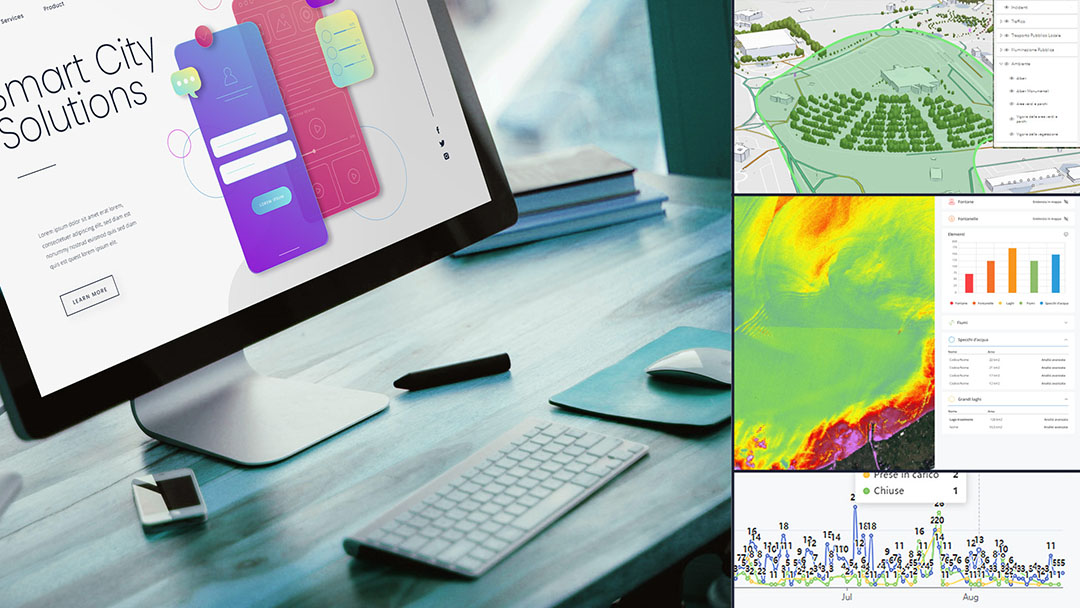
For the city of Perugia, WiseTown integrates its software infrastructure within existing systems in order to manage large amounts of data from different sources such as geographic information systems, satellite imagery, IoT sensors, Open Data and other existing services giving access to a single intelligent system for data management and analysis.
The use of WiseTown within the municipality’s control and data management systems aligns Perugia with the technological tools available in European capitals. This standardization enables information management and the integration of new applications, triggering virtuous collaborations between cities, universities and research centers.
building the Smart City
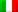
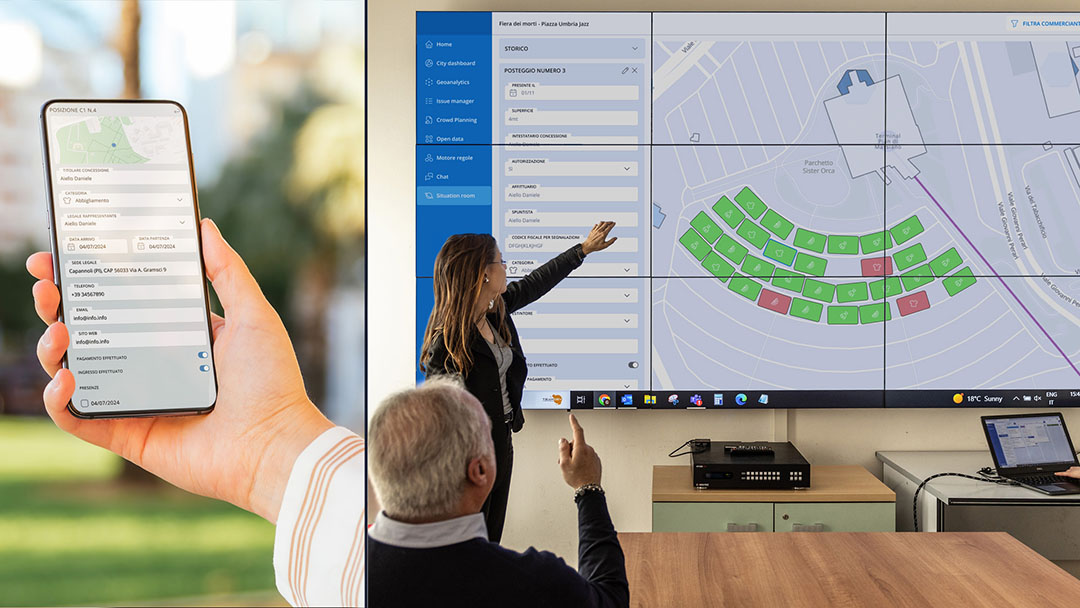
The smart city enabling infrastructure developed by WiseTown and declined for the Umbrian capital collects data from different sources: the Geographical Information System used by the municipality, IoT sensors, monitoring systems installed in the city, Open Data, historical data and those derived from applications in use in PA and by external parties.
Among the interaction components, WiseTown Geoanalytics, is the one dedicated to PA decision support. The component is in fact dedicated to spatially-based data analysis. WiseTown Situation Room, on the other hand, allows monitoring a specific geographic area in a given time interval, such as in the case of important city events, while WiseTown Situation Room optimizes the collection and management of reports that reach the PA from citizens. These are just some of the components that complete the WiseTown offer for the Municipality of Perugia, which, through a structured path of specific training, is accompanied by the process of appropriation of data processing tools.
the benefits: Smart City and Smart Community
WiseTown is the solution to the structural technological criticalities of Perugia, a city that receives a large amount of data from multiple departments of the administration, but which is poorly shared due to the lack of common standards. The city of Perugia is thus equipped with a range of solutions already approved at European level, with standardization that leads to optimization of costs and resources, harmonization of technologies, and achievement of service quality levels in line with the policies of large European cities.
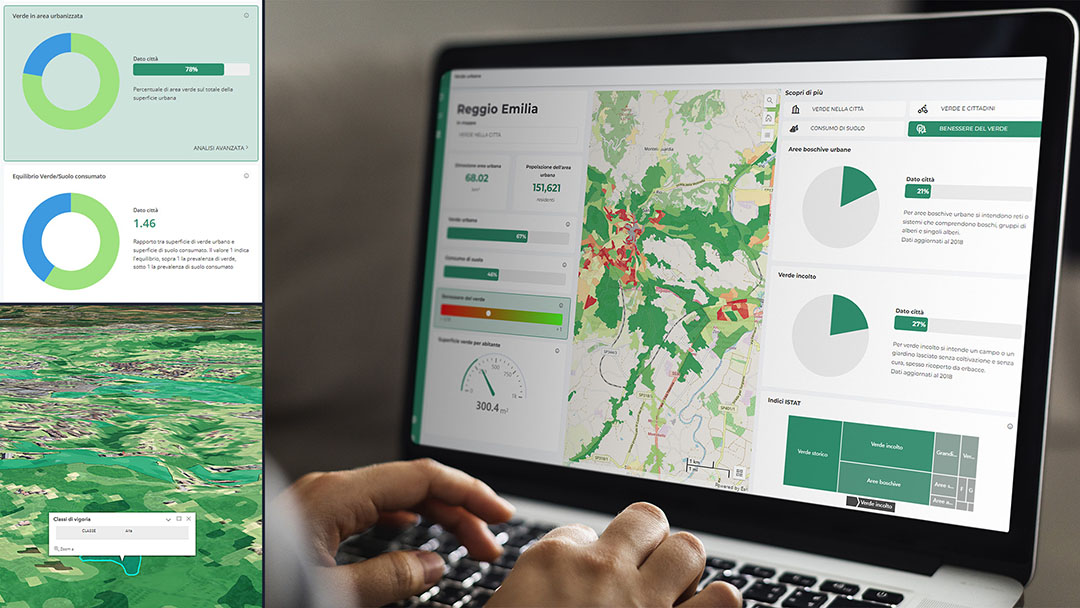
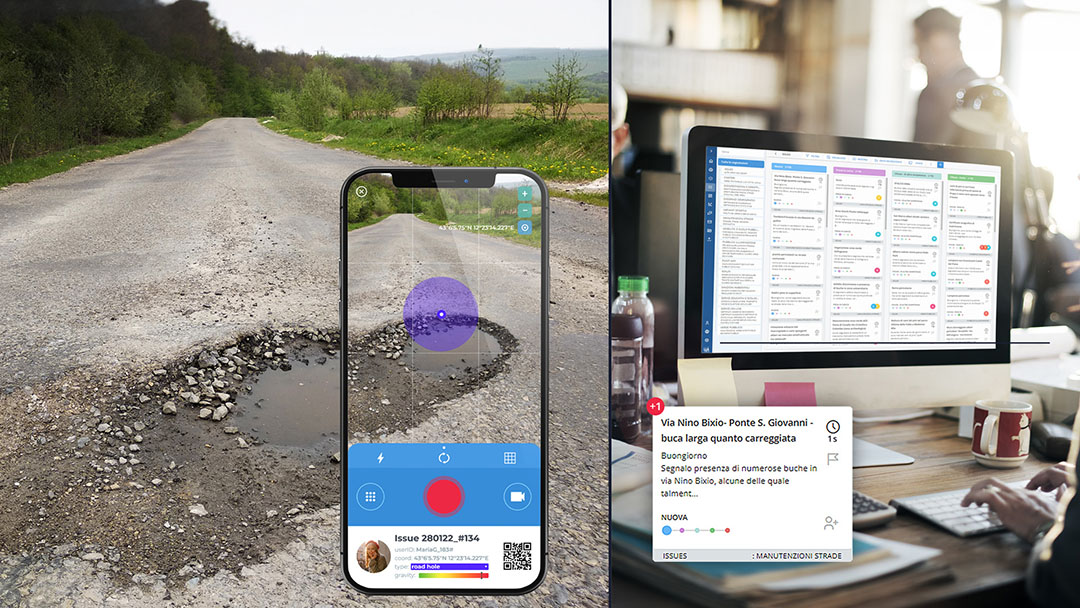
In the relationship between the community and the administration, WiseTown brings considerable benefits, allowing the adoption of useful tools to respond effectively and efficiently to the needs of citizens and to stimulate forms of active participation in the social and political life of the city. Among the many services offered, there is also the development of an App for reporting critical issues, thanks to which the citizen becomes the spokesperson for the city’s problems, generating an “issue” that is automatically converted into a “task” and assigned to the right department of the administration. A process that certainly strengthens the relationship of trust between decision-makers and citizens.
Project realised for the Municipality of Perugia
Perugia is the capital city of the Umbria Region, famous worldwide for its cultural, historical and artistic wealth; it has a population of around 165,000 inhabitants and is one of the first Italian municipalities in terms of territorial extension. On the occasion of the Smart City Expo World Congress in Barcelona in 2021, it presented its transformation path into a Smart City, launched with the support of WiseTown.
Fiware, the European Smart City technology giant, presented the WiseTown project for Perugia among its Impact Stories.
Contribution to sustainable urban development
The project aims to contribute to the achievement of the following Sustainable Development Goals of the 2030 Agenda, defined and promoted by the United Nations:
SDG 9. Building resilient infrastructure, promoting inclusive and sustainable industrialisation and fostering innovation
smart city solutions
Customizable modules that support administrators in developing a sustainable, safe, inclusive and participatory urban ecosystem.